Remediating security vulnerabilities
Vulnerabilities have a remediation status assigned to them. A new vulnerability can have a status of New, Needs Review, Patched, or Duplicate.
The following table describes each remediation status and whether a vulnerability with this status is included in the security risk calculations:
| Remediation Status | Included in Security Risk Calculation? | Definition |
|---|---|---|
| Duplicate | No | This vulnerability is a duplicate. |
| Ignored | No | The vulnerability has been ignored. |
|
Known Affected |
Yes | Actions are recommended to remediate or address this vulnerability. |
|
Known Not Affected |
No | A justification must be provided to ensure that the decision is properly documented. |
| Mitigated | No | The vulnerability has been mitigated. |
| New | Yes | Black Duck has determined that a vulnerability affects this component version. |
|
Needs Review |
Yes | Black Duck cannot determine if a
vulnerability definitely affects this component version. This can occur when a component version is known to contain a vulnerability, but it cannot be determined whether the patch or sub-version being used is affected by this vulnerability. |
| Patched | No | The vulnerability in this version of a Linux
distribution package has been patched. Although a vulnerability has been reported on the overall component version, the vulnerability does not affect this specific matched version as the version has been patched from the source from where it came. |
| Remediation Required | Yes | Remediation is required for the component version. |
| Remediation Complete | No | Remediation for the vulnerability is complete. |
| Under Investigation | Yes | It is not yet known if the product versions are affected by the vulnerability, but an update will be provided in a later release. |
Remediating a vulnerability
You may wish to change the remediation status after reviewing the severity of the vulnerability. Black Duck can help you determine which version you should use when a component has a vulnerability. Black Duck helps you to understand your options when a component has a security vulnerability.
You can remediate a vulnerability for current projects or set a global remediation status that applies to new instances of that vulnerability when that component appears on new BOMs.
Only users with the appropriate role can remediate vulnerabilities.
To remediate vulnerabilities for current projects:
Use this method to identify and remediate the vulnerabilities affecting a specific project version.
-
Log in to Black Duck SCA.
-
Select the project name using the Watching or My Projects dashboard. The Project Name page appears.
-
Select the version name to open the Components tab and view the BOM.
-
Select the Vulnerability tab which lists all vulnerabilities for this project version.
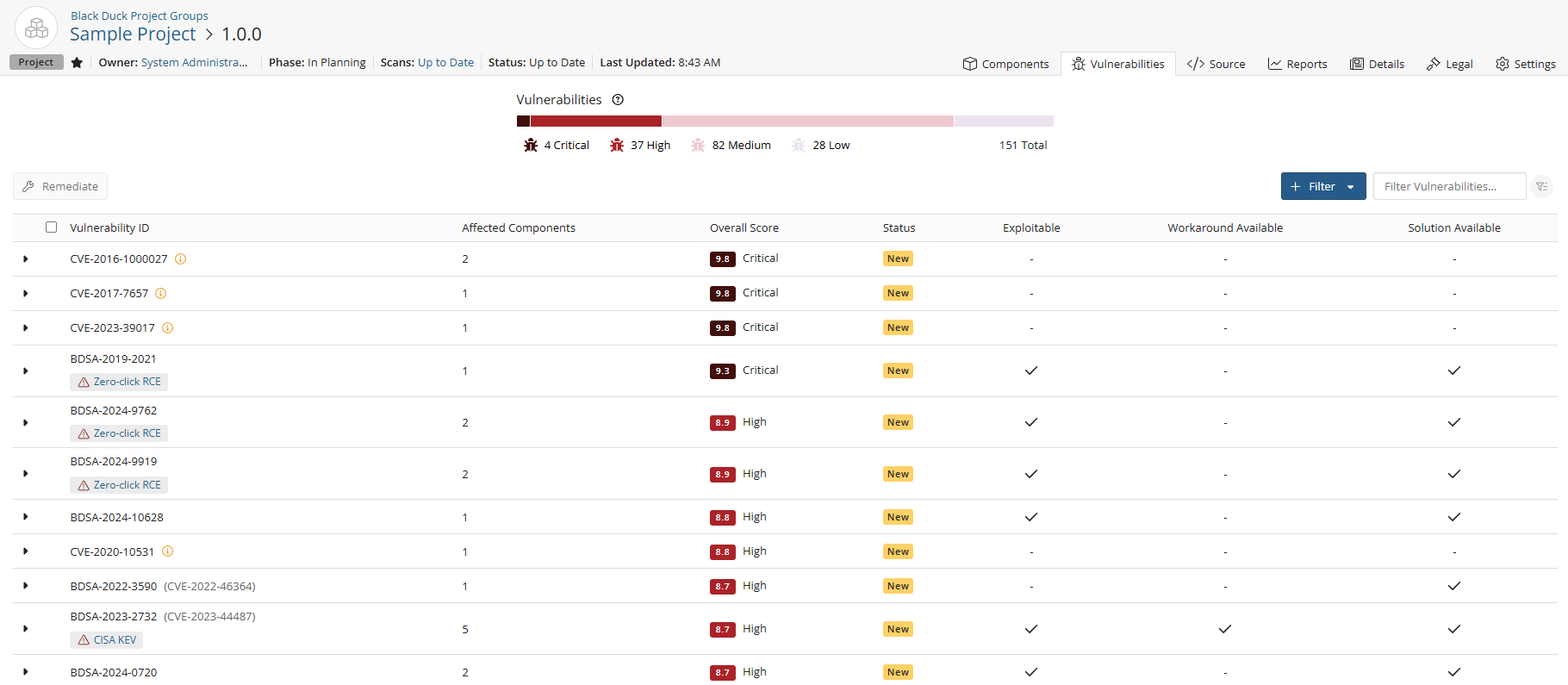
-
Click the
 icon in the table next to the vulnerability to expand the row. A brief
description, additional information, and fields to remediate the vulnerability appear.
icon in the table next to the vulnerability to expand the row. A brief
description, additional information, and fields to remediate the vulnerability appear. -
Click the
 next to a component to open the Remediate Vulnerability modal. From
here, you can update the following fields:
next to a component to open the Remediate Vulnerability modal. From
here, you can update the following fields:-
Status. See the table above for status definitions.
-
Status Justification. If "Known Not Affected" is the selected remediation, you must provide a justification for it. You can choose from the following:
-
Component not present. The vulnerable component is not included in the product.
-
Vulnerable code not present. The specific vulnerable code is not present in the component.
-
Vulnerable code cannot be controlled by adversary. The vulnerable code is present but cannot be controlled or exploited by an attacker.
-
Vulnerable code not in execute path. The vulnerable code exists but cannot be executed in the product's operational context.
-
Inline mitigations already exist. Built-in security measures are already in place, preventing the exploitation of the vulnerability.
-
-
Remediation: If "Known Affected" is the selected remediation, you must provide a remediation option. You can choose from the following:
-
Mitigation: The product includes built-in protections that prevent exploitation of the vulnerability.
-
No fix planned: The vulnerability will not be fixed.
-
None available: There are no fixes available for this vulnerability.
-
Vendor fix: There is an update by the vendor to address the vulnerability.
-
Workaround: There is a workaround available to fix the problem.
-
-
Target Date. This refers to the planned or intended deadline by which a vulnerability is expected to be remediated. It's often set based on the severity of the vulnerability, risk assessments, and your organization's security policies.
-
Actual Date. This is the date when the vulnerability is actually remediated or mitigated. It may differ from the target date depending on various factors, such as resource availability, complexity of the issue, or unexpected delays.
-
Comments. Any additional details or information regarding the vulnerability.
-
Remediating vulnerability by origin
To remediate vulnerabilities for this and/or additional project versions by origin, click the
![]() icon in the table next to the vulnerability to expand the row and then
click the View BDSA record or View CVE record link in the
Description box. Doing so will open the vulnerability's BDSA record or CVE record page.
icon in the table next to the vulnerability to expand the row and then
click the View BDSA record or View CVE record link in the
Description box. Doing so will open the vulnerability's BDSA record or CVE record page.
From here, you can view the projects affected by this vulnerability by selecting the Affected Projects tab. See the BDSA record or CVE record links above for more detailed instructions on how to remediate vulnerabilities by origin.
